2. Create a local cluster
Note
This Docker Quick Start is based on the new yugabyted server. You can refer to the older yb-docker-ctl based instructions in the v2.0 docs.
Note that yugabyted currently supports creating a single-node cluster only. Ability to create multi-node clusters is under active development.
1. Create a local cluster
To create a 1-node cluster with a replication factor (RF) of 1, run the command below.
$ docker run -d --name yugabyte -p7000:7000 -p9000:9000 -p5433:5433 -p9042:9042\
yugabytedb/yugabyte:latest bin/yugabyted start\
--daemon=false
As per the above docker run command, the data stored in YugabyteDB is not persistent across container restarts. If you want to make YugabyteDB persist data across restarts then you have to add the volume mount option to the docker run command as shown below.
docker run -d --name yugabyte -p7000:7000 -p9000:9000 -p5433:5433 -p9042:9042\
-v ~/yb_data:/home/yugabyte/var\
yugabytedb/yugabyte:latest bin/yugabyted start\
--daemon=false
Clients can now connect to the YSQL and YCQL APIs at localhost:5433 and localhost:9042 respectively.
2. Check cluster status
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
5088ca718f70 yugabytedb/yugabyte "bin/yugabyted start…" 46 seconds ago Up 44 seconds 0.0.0.0:5433->5433/tcp, 6379/tcp, 7100/tcp, 0.0.0.0:7000->7000/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9000->9000/tcp, 7200/tcp, 9100/tcp, 10100/tcp, 11000/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9042->9042/tcp, 12000/tcp yugabyte
3. Check cluster status with Admin UI
The yb-master Admin UI is available at http://localhost:7000 and the yb-tserver Admin UI is available at http://localhost:9000. To avoid port conflicts, you should make sure other processes on your machine do not have these ports mapped to localhost.
Overview and YB-Master status
The yb-master home page shows that you have a cluster (or universe) with Replication Factor of 1 and Num Nodes (TServers) as 1. The Num User Tables is 0 since there are no user tables created yet. YugabyteDB version number is also shown for your reference.
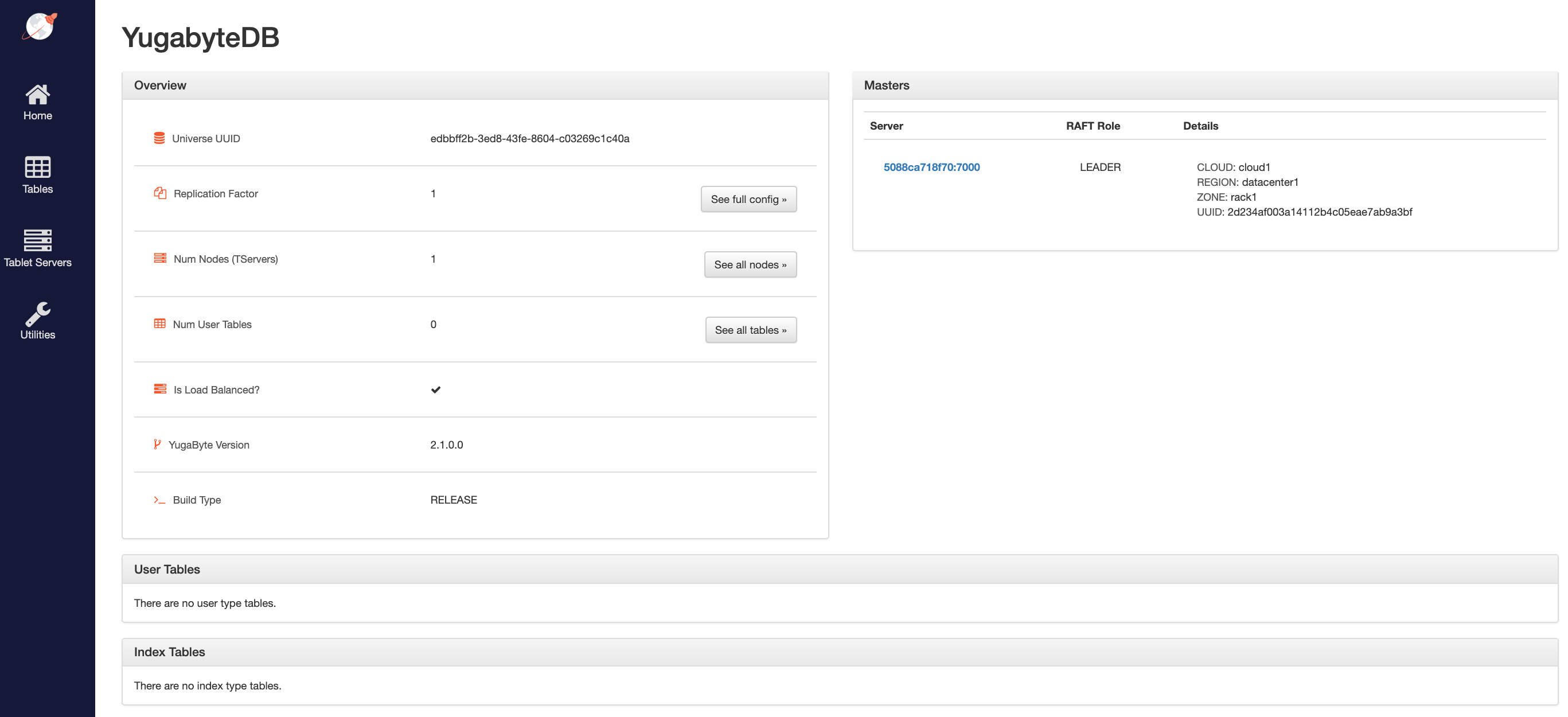
The Masters section highlights the cloud, region and zone placement for the yb-master servers.
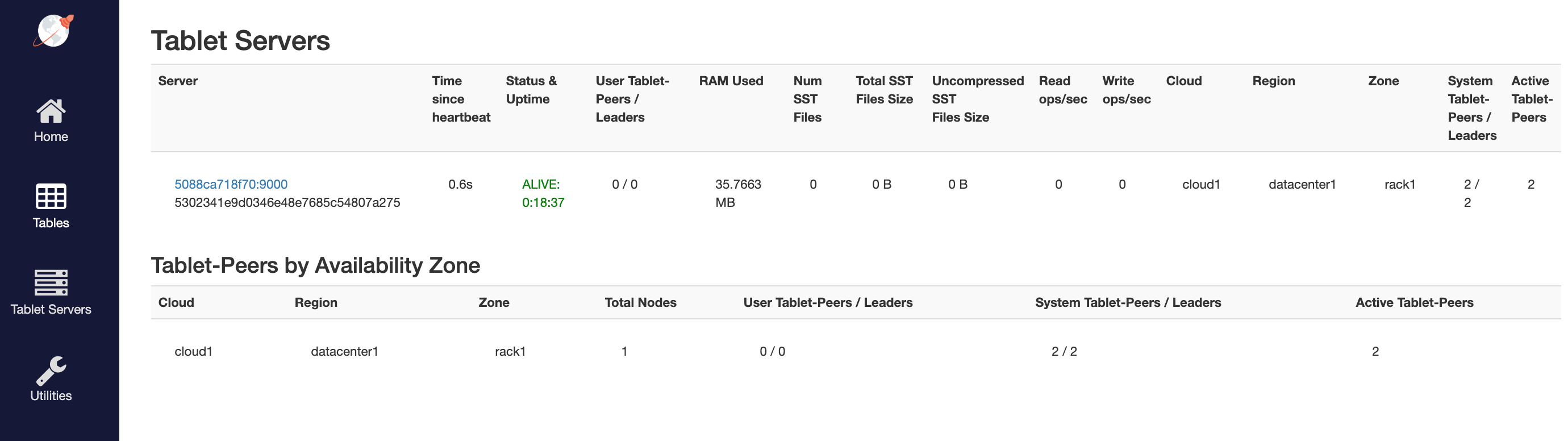
YB-TServer status
Clicking on the See all nodes takes us to the Tablet Servers page where you can observe the 1 tserver along with the time since it last connected to this master via regular heartbeats.
Next step
Explore YSQL