Create a multi-zone universe
This section will describe how to create a universe in one geographic region across multiple availability zones. We will examine the various nodes created by the Yugabyte Platform, run some workloads against this universe and take a look at the metrics against the running universe.
1. Create the universe
If there are no universes created yet, the Dashboard page will look like the following. Click Create Universe to create the universe.
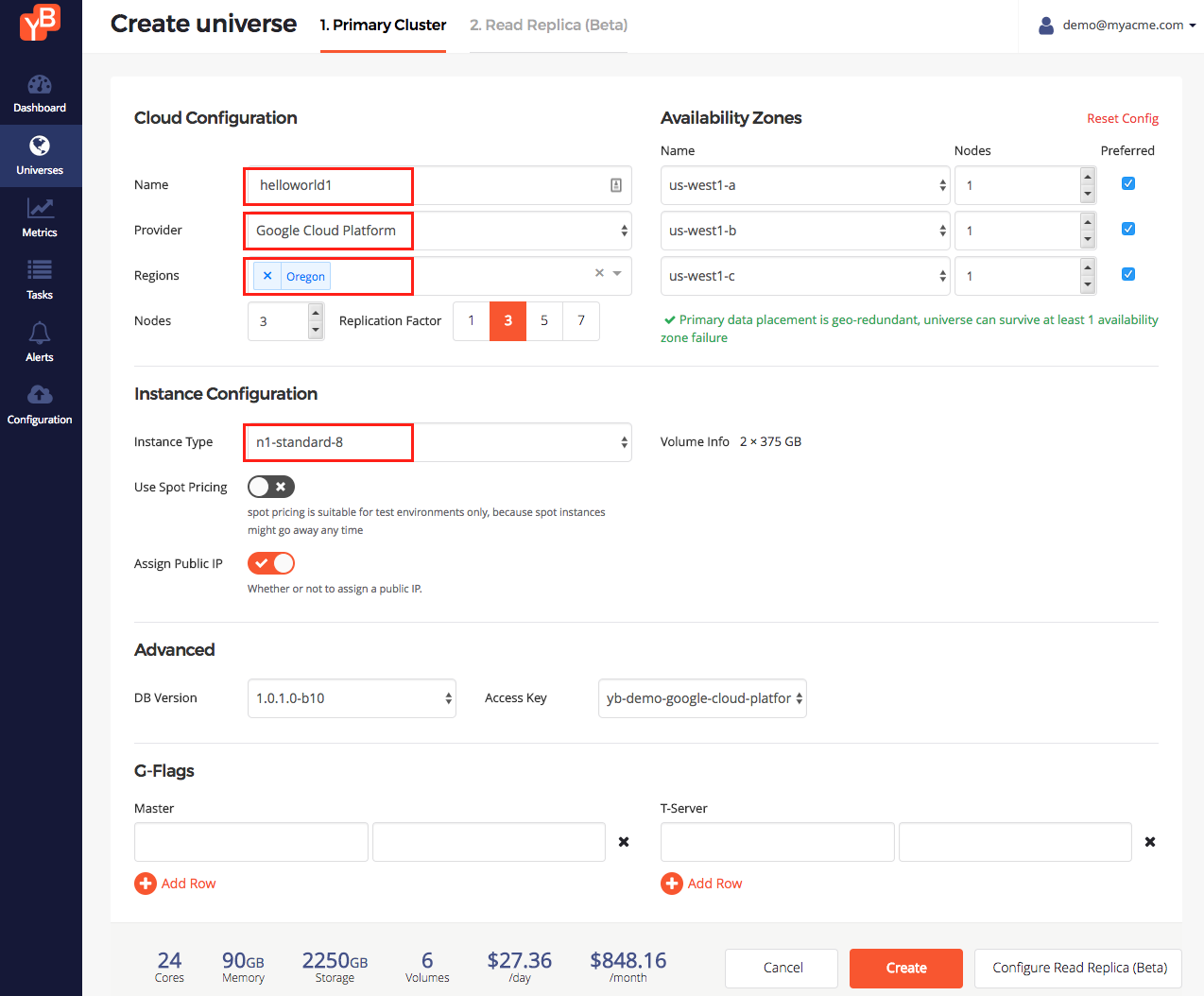
Enter your intent
The Provider, Regions and Instance Type fields were initialized based on the cloud providers configured. As soon as Provider, Regions and Nodes are entered, an intelligent Node Placement Policy kicks in to specify how the nodes should be placed across all the Availability Zones so that maximum availability is guaranteed.
We are going to enter the following values to create a multi-zone universe on GCP provider:
- Enter a universe name (helloworld1)
- Enter the region (Oregon)
- Change instance type (n1-standard-8)
All other options as set to the default values (replication factor = 3, number of nodes = 3). Click Create.
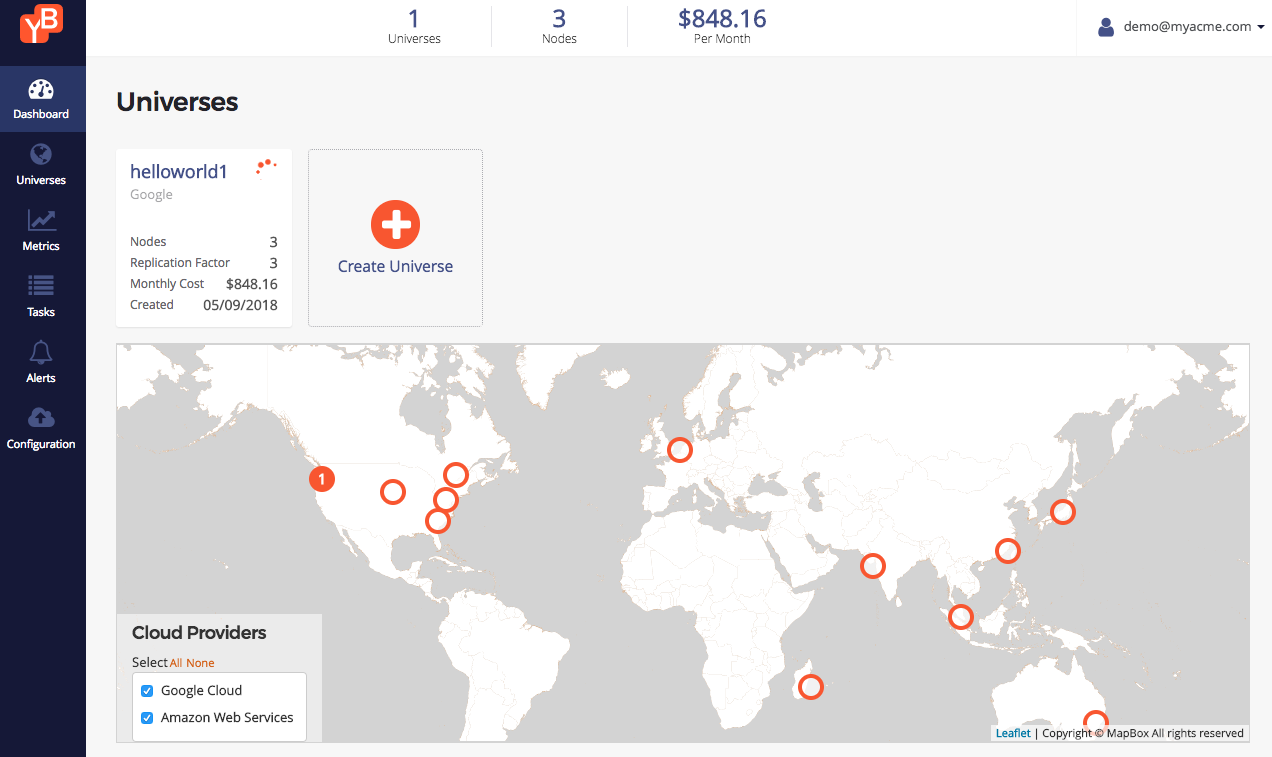
Here's how a Universe in Pending state looks like.
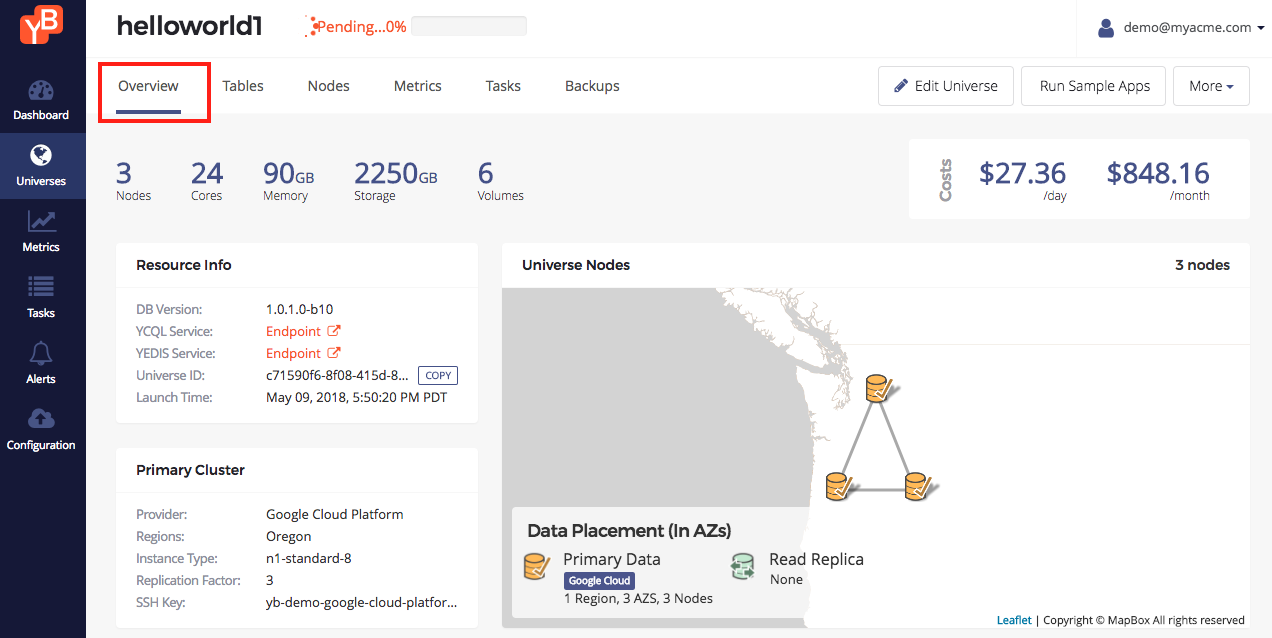
2. Examine the universe
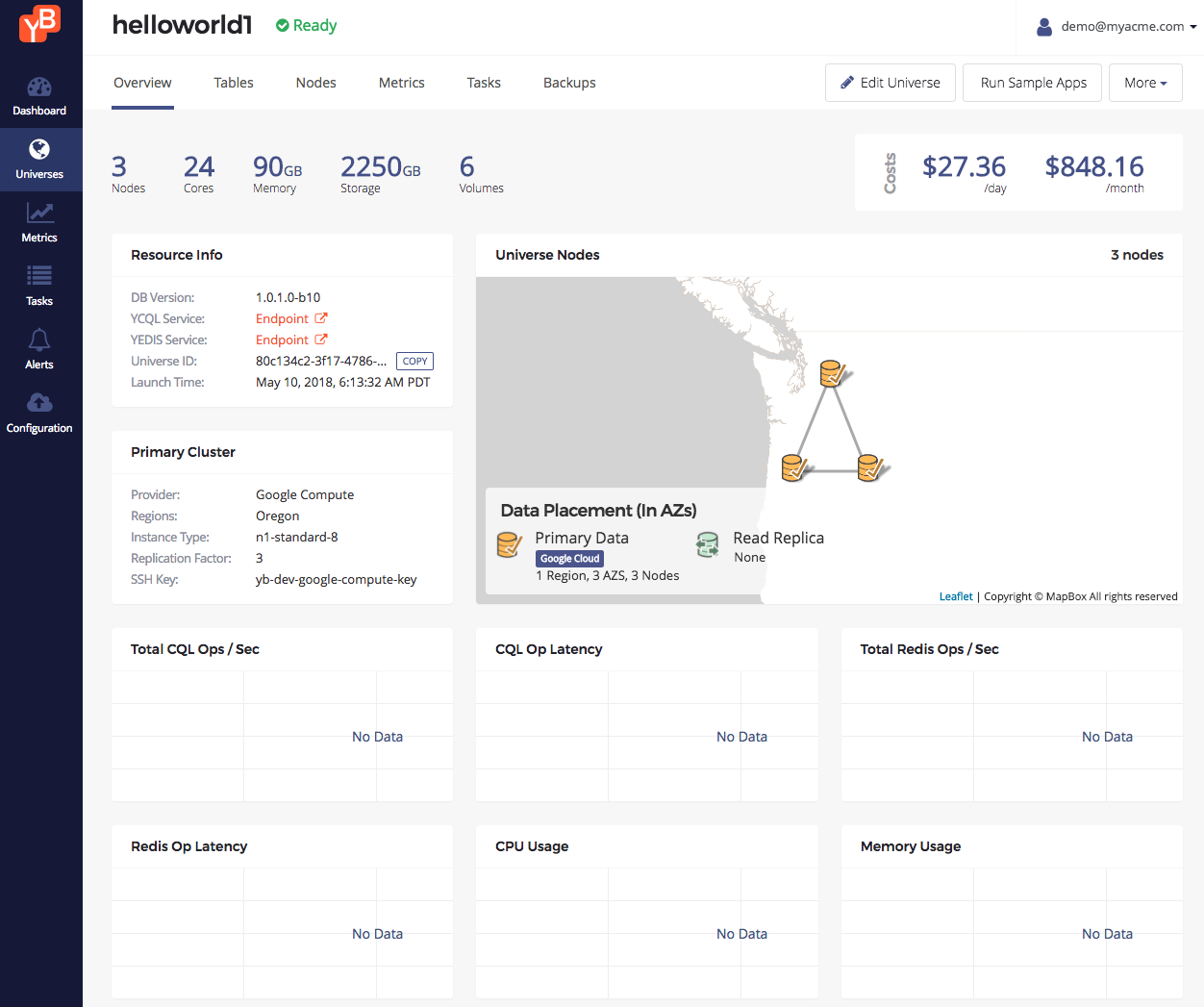
Universe overview
The overview tab has a lot of information at a glance about the universe.
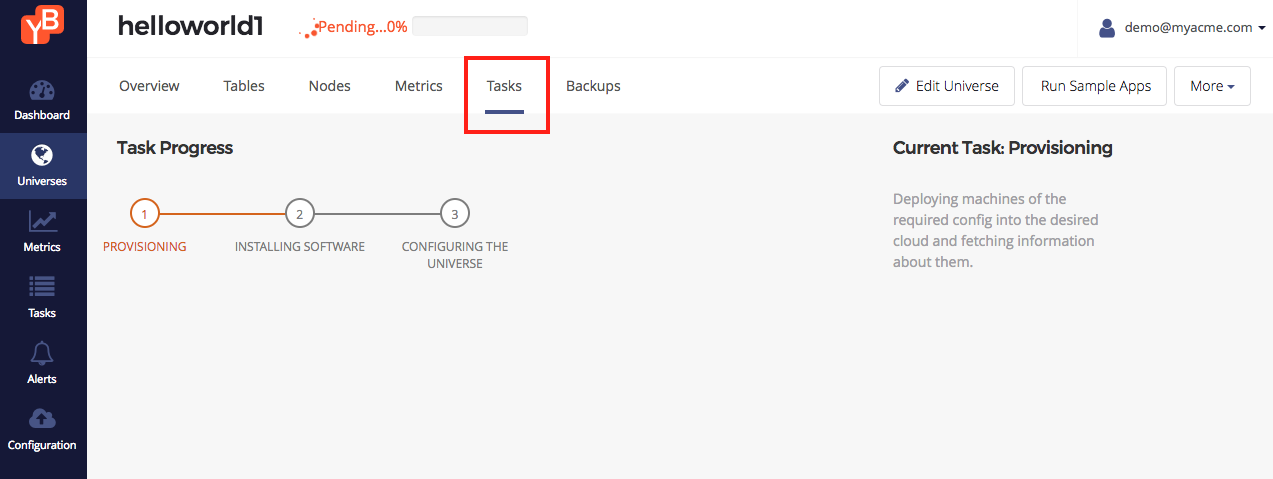
Tasks level tracking for a Universe
The tasks tab shows the state of tasks currently running, as well as the tasks that have run in the past against this universe.
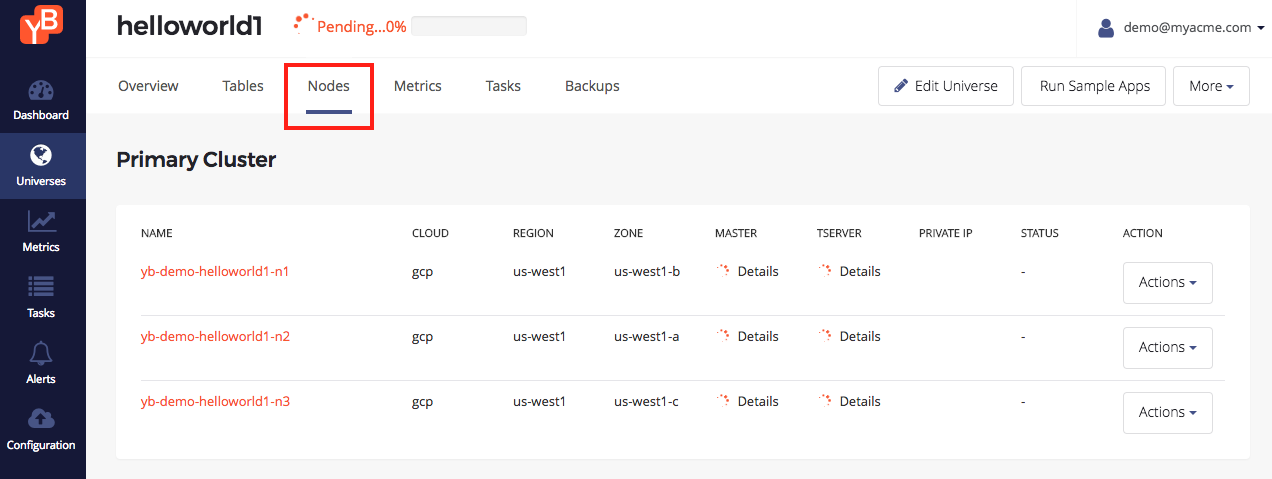
Nodes underlying a universe
You can browse to the Nodes tab for the universe to see a list of nodes - in the screenshot below the cloud provider instances are still being created.
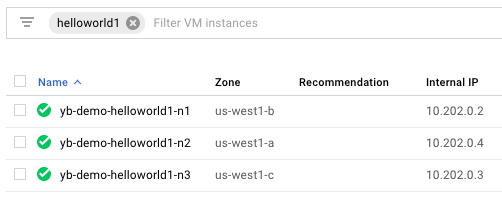
Cloud provider instances for the universe
Browse to the cloud provider's instances page. In this example, since you are using Google Cloud Platform as the cloud provider, browse to Compute Engine -> VM Instances and search for instances that have helloworld1 in their name. You should see something as follows.
3. Connect to a database node
Once the universe is ready, the overview tab should look as follows.
Browse to the Nodes tab to find the nodes. This lists the ip addresses of the nodes once they are created and configured. Click on the Connect button as shown below.
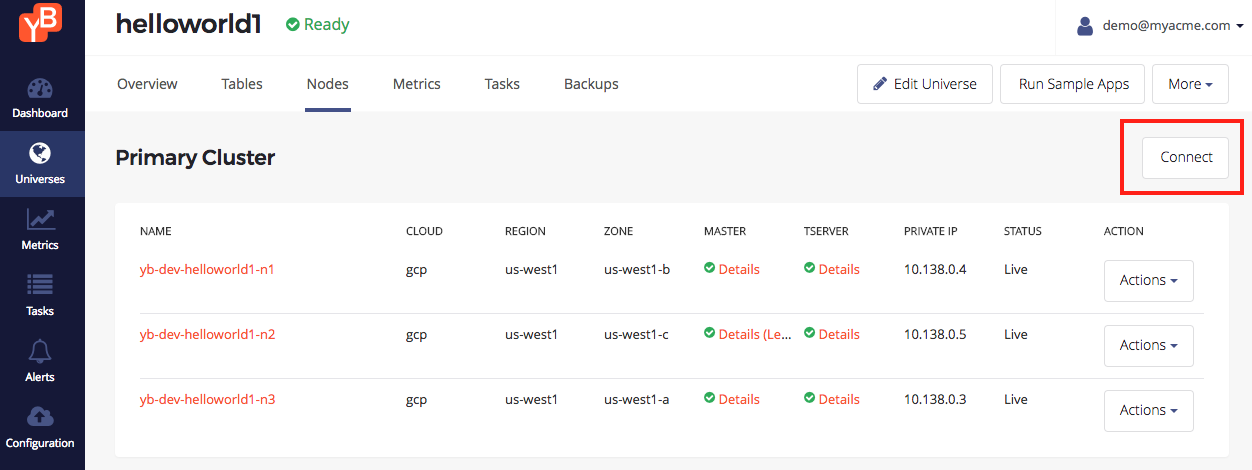
This should bring up a dialog showing how to connect to the nodes.
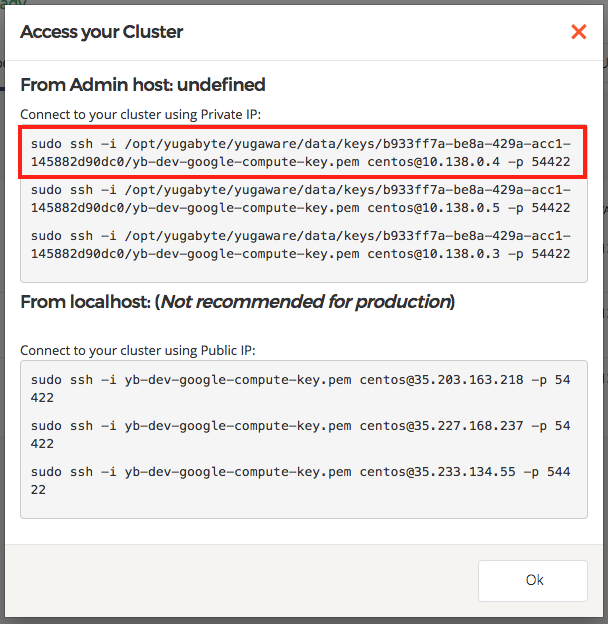
Copy the first command (highlighted above) and run it from the Yugabyte Platform server. This will connect us to the first node, yb-dev-helloworld1-n1.
centos@yugaware-1:~$ sudo ssh -i /opt/yugabyte/yugaware/data/keys/b933ff7a-be8a-429a-acc1-145882d90dc0/yb-dev-google-compute-key.pem centos@10.138.0.4
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
[centos@yb-dev-helloworld1-n1 ~]$
4. Running workloads
Yugabyte Platform comes with a pre-packaged set of sample applications. You will run a simple key-value workload against the YCQL API and the YEDIS API.
Prerequisites
- Install Java
You can do this as shown below.
$ sudo yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk.x86_64 -y
- Switch to the
yugabyteuser
$ sudo su - yugabyte
- Export the
YCQL_ENDPOINTSenv variable
Export an environment variable telling the IP addresses for nodes in the cluster. Browse to the Universe Overview tab in the Yugabyte Platform console and click YCQL Endpoints. A new tab opens with a list of IP addresses.
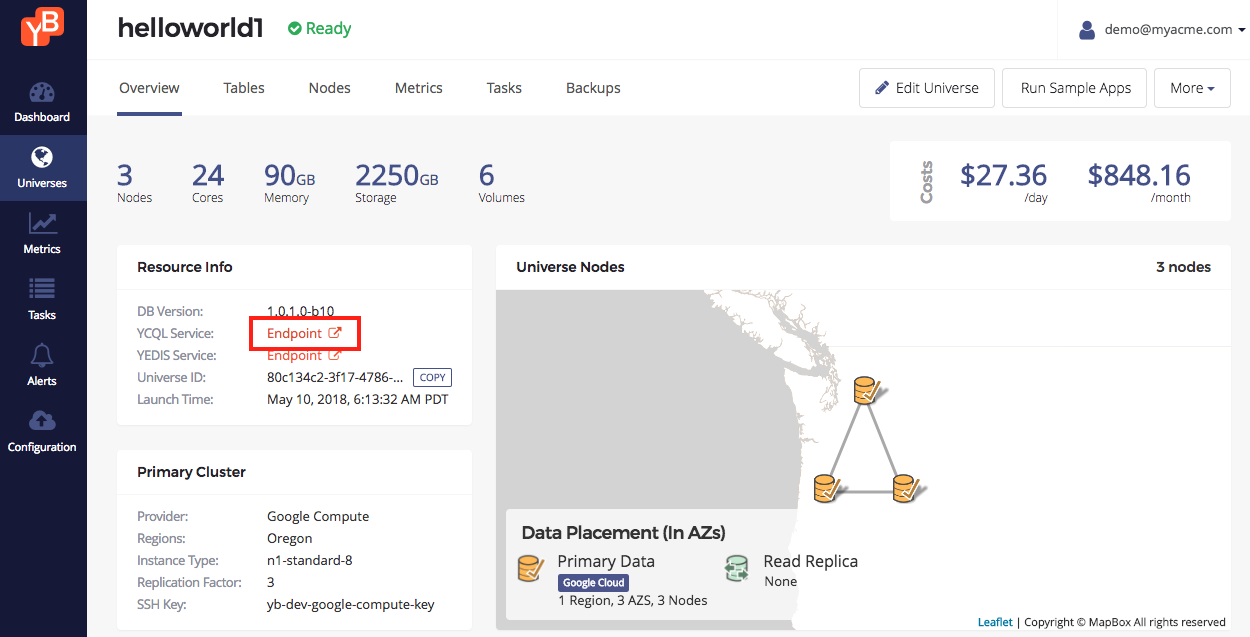
Export this into a shell variable on the database node yb-dev-helloworld1-n1 you had connected to. Remember to replace the IP addresses below with those shown by the Yugabyte Platform console.
$ export YCQL_ENDPOINTS="10.138.0.3:9042,10.138.0.4:9042,10.138.0.5:9042"
- Export the
YEDIS_ENDPOINTSenv variable
Repeat the same process for the YEDIS endpoints.
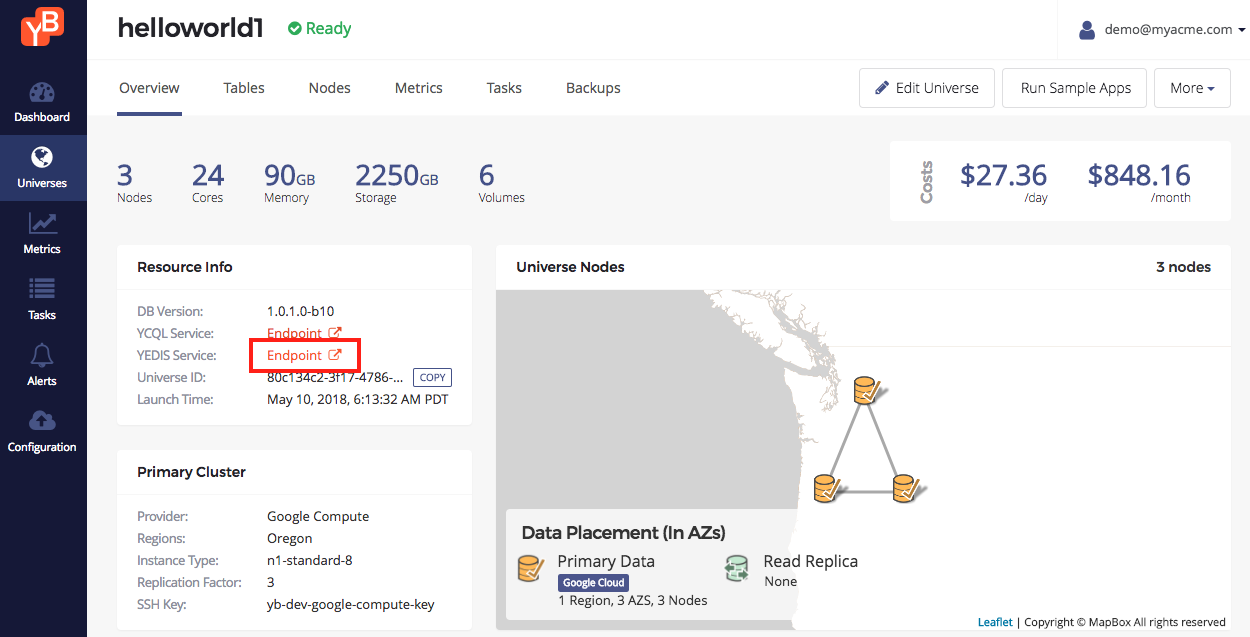
Export an environment variable for the YEDIS endpoints.
$ export YEDIS_ENDPOINTS="10.138.0.3:6379,10.138.0.4:6379,10.138.0.5:6379"
Run the CassandraKeyValue workload
To start the workload, run the following command.
$ java -jar /home/yugabyte/tserver/java/yb-sample-apps.jar \
--workload CassandraKeyValue \
--nodes $YCQL_ENDPOINTS \
--num_threads_write 2 \
--num_threads_read 32 \
--value_size 128 \
--num_unique_keys 10000000 \
--nouuid
The sample app will print some output and settle into reporting some stats in the steady state.
Created table: [CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS CassandraKeyValue (k varchar, v blob, primary key (k));]
...
Read: 47388.10 ops/sec (0.67 ms/op), 816030 total ops | Write: 1307.80 ops/sec (1.53 ms/op), 22900 total ops
Read: 47419.99 ops/sec (0.67 ms/op), 1053156 total ops | Write: 1303.85 ops/sec (1.53 ms/op), 29420 total ops
Read: 47220.98 ops/sec (0.68 ms/op), 1289285 total ops | Write: 1311.67 ops/sec (1.52 ms/op), 35979 total ops
Browse to the Metrics tab of the universe in the Yugabyte Platform console. You should be able to see the metrics show up. The metrics tab displays a variety of metrics, a few are shown in the screenshot below. Note that these numbers (server side metrics) tally with what the load tester reports (client side metrics).
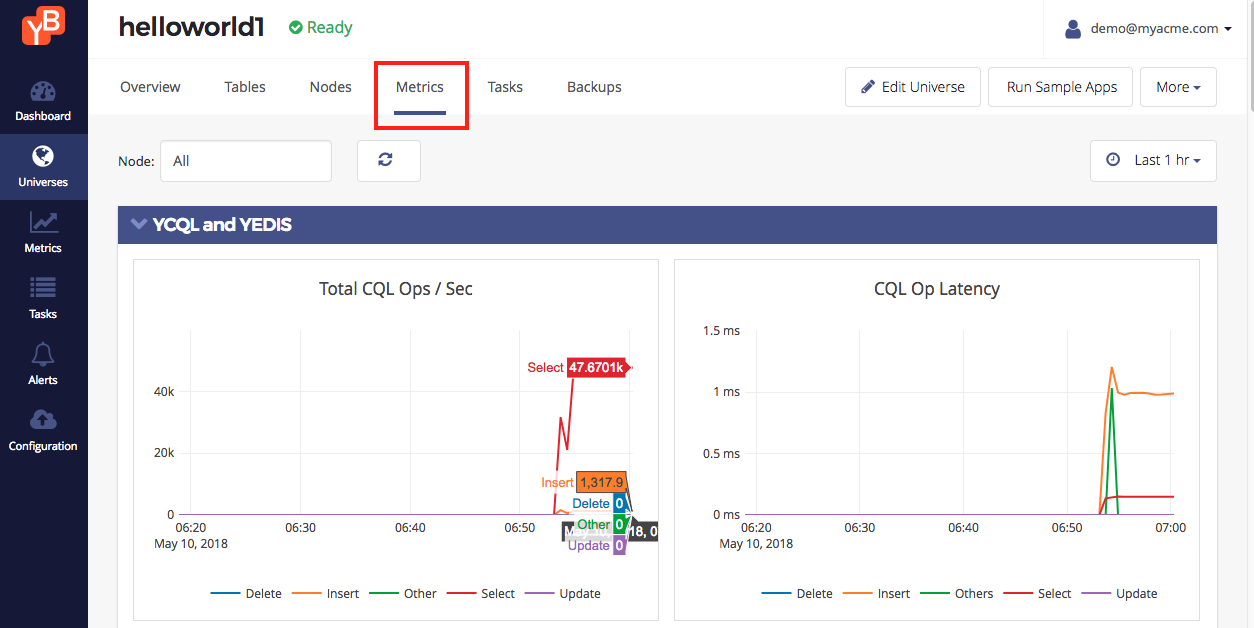
It is also possible to view the metrics at a per-node level as shown below.
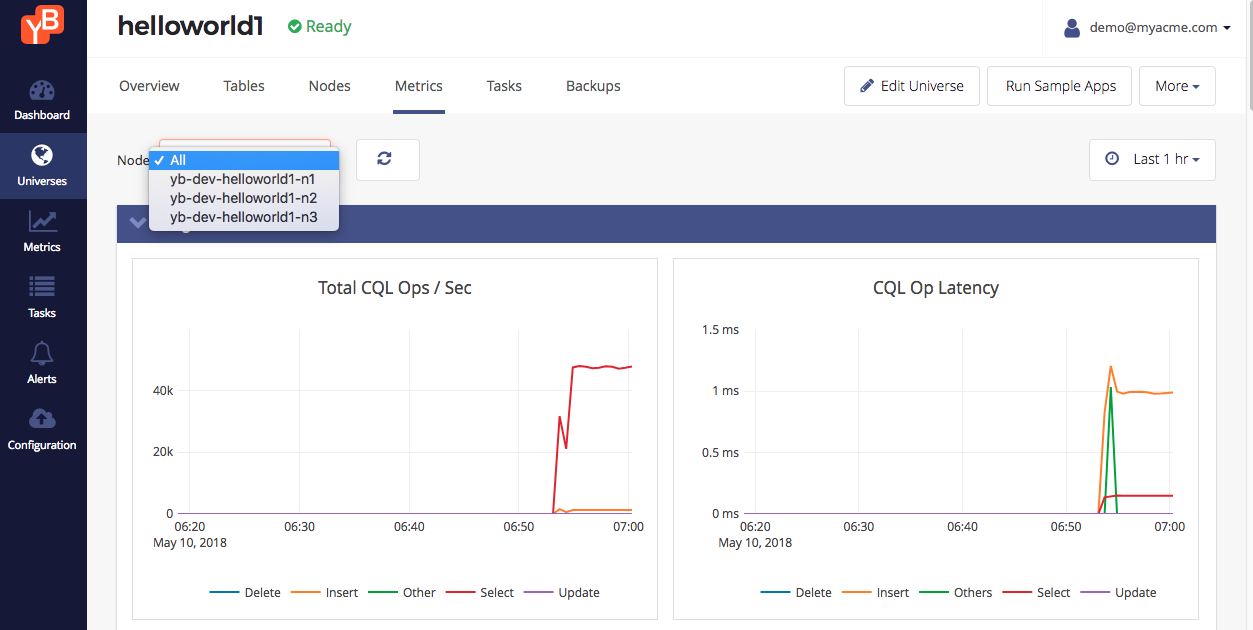
Let us stop the load tester and run a yedis workload.
Run the RedisKeyValue workload
To start the workload, run the following command.
$ java -jar /home/yugabyte/tserver/java/yb-sample-apps.jar \
--workload RedisKeyValue \
--nodes $YEDIS_ENDPOINTS \
--num_threads_write 2 \
--num_threads_read 32 \
--value_size 128 \
--num_unique_keys 10000000 \
--nouuid
The sample application will print some output and settle into reporting some stats in the steady state.
Read: 50069.15 ops/sec (0.64 ms/op), 657550 total ops | Write: 1470.87 ops/sec (1.36 ms/op), 18849 total ops
Read: 50209.09 ops/sec (0.64 ms/op), 908653 total ops | Write: 1454.87 ops/sec (1.37 ms/op), 26125 total ops
Read: 50016.18 ops/sec (0.64 ms/op), 1158794 total ops | Write: 1463.26 ops/sec (1.37 ms/op), 33443 total ops
Browse to the Metrics tab of the universe in the Yugabyte Platform console. You should be able to see the metrics show up. The metrics tab displays a variety of metrics, a few are shown in the screenshot below. Note that these numbers (server side metrics) tally with what the load tester reports (client side metrics).
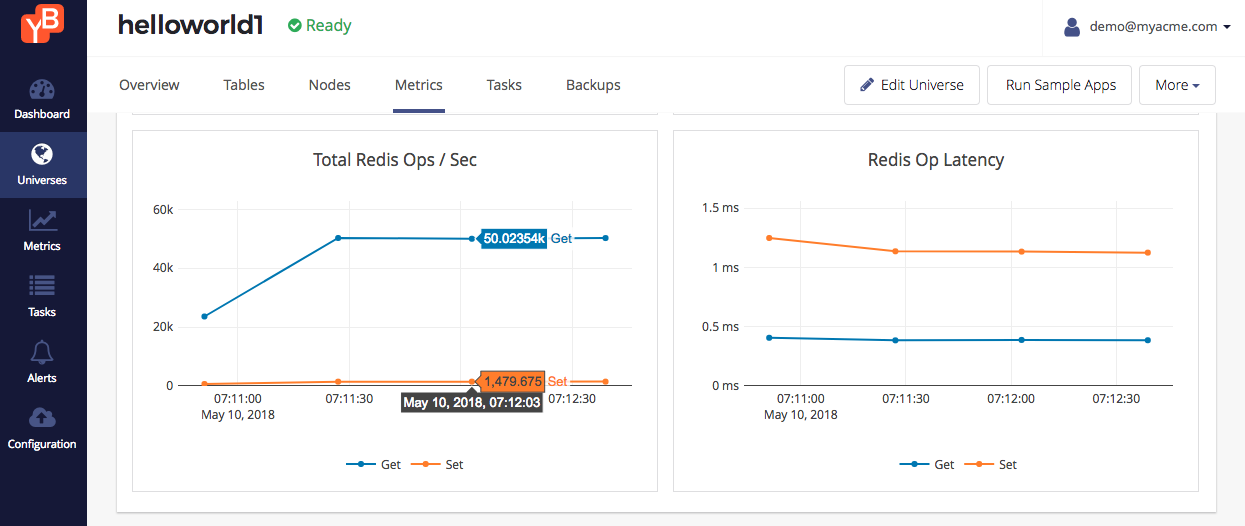
Stop the sample application.
5. Examine the data
You can connect to the YCQL service by running the following command.
$ /home/yugabyte/tserver/bin/ycqlsh <ip address of the node>
You can view the table schema as well as the data entered as shown below.
ycqlsh> DESCRIBE ybdemo_keyspace.cassandrakeyvalue;
CREATE TABLE ybdemo_keyspace.cassandrakeyvalue (
k text PRIMARY KEY,
v blob
) WITH default_time_to_live = 0;
ycqlsh> SELECT * FROM ybdemo_keyspace.cassandrakeyvalue LIMIT 5;
k | v
------------+-----------------------------------------
key:101323 | 0x4276616c3a3130313332336be1dd6597e2...
key:159968 | 0x4276616c3a3135393936381ed99587c08f...
key:24879 | 0x4276616c3a3234383739054071b34c3fb6...
key:294799 | 0x4276616c3a3239343739398b312748e80e...
key:297045 | 0x4276616c3a32393730343525764eedee94...
(5 rows)
You can connect to the YEDIS service by running the following command.
$ /home/yugabyte/tserver/bin/redis-cli -h <ip address of the node>
You can view the data by running the following commands.
10.138.0.4:6379> GET key:0
"Bval:0\x1b\x942\xea\xf0Q\xd1O\xdb\xf8...=V"
10.138.0.4:6379> GET key:1
"Bval:1\t\x1e\xa0=\xb66\x8b\x8eV\x82...,c"
10.138.0.4:6379>